Hospitals in Canada must have reliable emergency power solutions to ensure patient safety and well-being. Emergency lighting battery packs are very crucial component of these backup systems, as they provide uninterrupted power supply to maintain operations and uphold high standards of patient care.
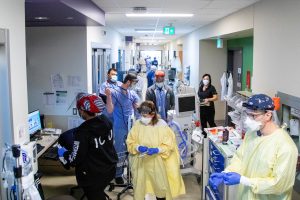
In Canada, harsh weather conditions and unforeseen power outages are common, making these batteries essential for maintaining operational efficiency. Flashers is crucial in hospitals for safety during power outages or crises which improves patient safety, enhances recovery processes & increasingly prevalent in healthcare settings, providing reliable illumination when regular lights fail.
Flashers is a crucial component in hospitals, providing lifesaving light during power failures or natural disasters. It marks escape routes and exits, ensuring safety for staff and patients. This technology allows medical teams to continue work uninterrupted, a crucial aspect of saving lives throughout history.
Emergency lighting battery packs are essential for safety and security in facilities, including hospitals. They provide backup powe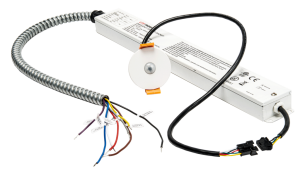 r to lighting fixtures when the main power supply fails, consisting of rechargeable batteries, control circuits, and wiring. It can be centralized battery systems or self-contained battery units. and have automatic activation, varying duration, and are compatible with LED lighting fixtures.
r to lighting fixtures when the main power supply fails, consisting of rechargeable batteries, control circuits, and wiring. It can be centralized battery systems or self-contained battery units. and have automatic activation, varying duration, and are compatible with LED lighting fixtures.
Regular testing and maintenance are required to ensure their functionality which can be installed during construction or retrofitted into existing lighting systems. Regulatory compliance is very essential, as they meet minimum standards set by authorities like the National Fire Protection Association and the Canadian Standards Association. The advantages of emergency lighting battery packs include enhanced safety, regulatory compliance, and operational continuity.
Emergency lighting systems are crucial for ensuring safety & security in various settings including hospitals and which include backup power sources like batteries or generators, provide illumination during power outages or emergencies. Types of emergency lighting include exit signs, emergency lights, stairwell lights, and pathway lighting. Backup power sources include rechargeable batteries or generators, which automatically supply power to emergency lighting fixtures during outages.
Hospitals in Canada are subject to safety regulations and standards established by various regulatory authorities. These include the National Building Code of Canada (NBCC), fire safety codes and standards from organizations like the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) and the Canadian Standards Association (CSA). Hospitals must hold fast to these regulations to ensure the safety and security of patients, staff, and visitors.
These standards cover fire detection, alarm systems, emergency lighting, hazard assessment, personal protective equipment, safe work practices, and emergency preparedness. Hospitals often undergo accreditation by organizations like Accreditation Canada or the Canadian Council on Health Services Accreditation (CCHSA). By ensuring compliance, hospitals can maintain a safe and secure environment while providing high-quality healthcare services.
In hospitals, they must protect themselves from legal liabilities by bonding to regulations, risk management programs, quality improvement initiatives, staff training, documentation practices, patient communication, insurance coverage, legal counsel, ethical standards compliance with regulations, risk management programs, quality improvement initiatives and so on.
Hospitals must minimize disruption to operations during emergencies to ensure patient care continuity, safety, and efficiency. They develop comprehensive emergency preparedness plans, invest in backup power systems, prioritize power distribution, implement protocols for patient care continuity, maintain effective communication, optimize resource management, conduct training and drills, and continuously evaluate and improve their emergency response capabilities.
These strategies include implementing robust emergency preparedness plans, investing in backup power systems, prioritizing patient care continuity, maintaining effective communication and coordination, optimizing resource management, conducting training and drills, and conducting post-incident evaluations to assess the effectiveness of their response. It also helps to ensure the safety, resilience, and reliability of hospital operations in the face of unforeseen challenges.
Hospitals use strategies like redundant systems, emergency preparedness plans, remote monitoring, cross-training, robust supply chain management, regular maintenance, and investing in modern technologies to minimize operational disruptions. They also implement predictive maintenance, energy efficiency measures, and outsourcing maintenance services. Life cycle cost analysis aid in informed decisions and ensuring efficient healthcare service delivery.
Hospitals are vital in enhancing patient comfort and security, promoting positive outcomes and satisfaction. They offer comfortable accommodations, effective pain management, personalized care plans, effective communication, emotional and psychosocial support, family-centered care, amenities, security measures, infection control practices. These facilities also implement physical security measures, patient identification protocols, infection control practices, and emergency preparedness plans.
Canadian hospitals rely on reliable emergency power solutions to ensure continuous operations and patient care in extreme weather conditions. These solutions include backup generators, UPS systems, battery backups, microgrids, energy storage systems, and energy management systems.
 Backup generators are standby power sources that automatically provide electricity to critical systems and equipment during power outages. They are typically fueled by diesel, natural gas, propane, or gasoline and are connected to the building’s electrical system through an automatic transfer switch (ATS).
Backup generators are standby power sources that automatically provide electricity to critical systems and equipment during power outages. They are typically fueled by diesel, natural gas, propane, or gasoline and are connected to the building’s electrical system through an automatic transfer switch (ATS).
They are typically installed on-site or nearby the facility and are connected to the building’s electrical system through an ATS. The capacity of a generator is measured in kilowatts (kW) or kilovolt-amperes (kVA).

Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) systems are electrical devices that provide backup power to equipment during power outages or voltage irregularities. They come in three types: offline/standby, line-interactive, and online/double-conversion.
They consist of a rectifier, battery bank, inverter, static switch, and monitoring system. UPS systems are installed in dedicated rooms or rack-mounted facilities, and regular maintenance is essential for reliable operation.
 Battery backup systems, also known as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), are essential for providing emergency power during outages or disruptions to the main power supply. They store electrical energy in chemical form and convert it to electrical power when needed.
Battery backup systems, also known as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), are essential for providing emergency power during outages or disruptions to the main power supply. They store electrical energy in chemical form and convert it to electrical power when needed.
When the main power supply fails or experiences voltage fluctuations, the system automatically switches to battery power, ensuring uninterrupted power supply to connected equipment or systems. They are commonly used for emergency lighting, critical equipment, and residential use.
Lithium-ion batteries are increasingly used due to their higher energy density, longer lifespan, faster charging times, and lower maintenance requirements. They also have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional lead-acid batteries.
Battery backup systems are often integrated with other backup power sources, such as generators, to provide comprehensive power backup solutions. Regular monitoring and maintenance are required to ensure proper functionality and reliability during emergencies. Regulatory compliance is also crucial to minimize risks to personnel and property.
Microgrids are localized energy systems that provide reliable power to specific areas or communities, enhancing energy security and grid stability. They can operate in grid-connected or islanded modes, improving energy efficiency and reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Energy storage systems (ESS) store electrical energy for later use, balancing supply and demand, integrating renewable energy sources, and providing backup power during outages. They can be deployed at various scales and support intermittent renewable energy sources.
Energy Management Systems (EMS) are software-based platforms that monitor, control, and optimize energy consumption and generation in buildings, facilities, or entire energy networks. They collect data from sensors, meters, and smart devices to analyze energy usage patterns, identify efficiency improvements, and optimize system performance.
EMS can automate tasks like demand response, load shifting, and equipment scheduling, reducing energy costs and enhancing operational efficiency. They provide real-time visibility into energy consumption, demand, and generation, enabling operators to make informed decisions and respond quickly to changes in energy conditions.
Emergency preparedness plans outline procedures, protocols, and responsibilities for responding to various emergencies, such as natural disasters, fires, medical emergencies, and security threats. They are developed based on risk assessments, regulatory requirements, and best practices in emergency management.
Key components include risk assessment, response procedures, roles and responsibilities, communication plans, training and drills, resource management, continuity of operations, and recovery and restoration procedures. Technology can be integrated into these plans to enhance response and coordination. Regular reviews and updates are necessary to reflect changes in risks, regulations, and organizational requirements.
In conclusion, Canadian hospitals rely on reliable emergency power solutions, particularly emergency lighting battery packs, to ensure continuous operation during critical situations like power outages or emergencies. Sanforce is a leading provider which offers innovative, efficient solutions tailored to Canadian hospitals’ unique needs.
These battery packs, with high energy density, extended lifespan, and rapid charging capabilities, ensure dependable performance during emergencies. Integrating it into emergency preparedness plans enhances resilience and readiness, complementing backup power sources like generators and UPS systems. The partnership between Canadian hospitals and Sanforce emphasizes prioritizing patient safety and ensuring continuous access to critical healthcare services.
Emergency lighting battery packs are devices designed to provide backup power to emergency lighting fixtures during power outages or disruptions. They work by storing electrical energy in batteries, which is then used to power the emergency lights when the main power supply fails.
Emergency lighting battery packs are crucial for Canadian hospitals to ensure the continuous illumination of critical areas during power outages or emergencies. They help maintain a safe environment for patients, staff, and visitors and ensure that essential operations can continue without interruption.
Canadian hospitals should consider features such as high energy density, extended battery life, rapid charging capabilities, and reliability in emergency lighting battery packs. Additionally, compatibility with existing lighting fixtures and ease of installation are important factors to consider.
The runtime of emergency lighting battery packs during a power outage depends on factors such as the capacity of the batteries, the energy efficiency of the lighting fixtures, and the level of illumination required. Hospitals should evaluate their specific needs and select battery packs with sufficient runtime to meet those requirements.
Yes, like any other electrical equipment, emergency lighting battery packs require regular maintenance to ensure proper functioning during emergencies. This may include periodic testing, battery inspections, and replacement of batteries or components as needed.
Emergency lighting battery packs are typically designed to be compatible with a wide range of lighting fixtures, including LED, fluorescent, and incandescent lights. Hospitals should verify compatibility with their specific lighting fixtures before purchasing battery packs.
Yes, emergency lighting battery packs can be integrated with other emergency power solutions such as generators and uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems to provide comprehensive backup power coverage for Canadian hospitals. This ensures redundancy and reliability in emergency power systems.
Canadian hospitals should ensure that emergency lighting battery packs comply with relevant regulations and standards, including those set forth by regulatory agencies such as Health Canada, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA), and provincial building codes. Compliance ensures the safety and reliability of emergency power systems.
Not sure what you required for your lightining project ?
Get in touch with us for FREE consultation.